KEY CIDER TERMS:
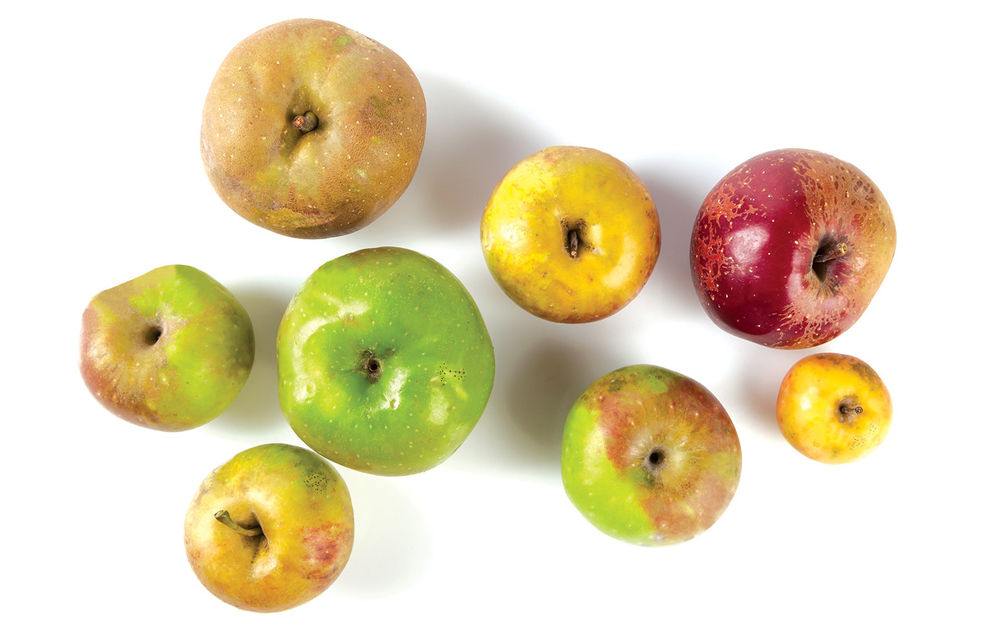
- Sharps – Apples that are low in tannin, and high in acid. (Typically New World)
- Sweets – Apples that are low in tannin and, and low in acid. (Typically New World and modern varities)
- Bitter Sweets – Apples that are high in tannins, and low in acids. (Typically Old World)
- Bitter Sharps – Apples that are high tannins, and high in acids (Typically native apples and heirloom varieties.
- Aromatic – Apples that have qualities that enhance the nose or aromas of your cider.
- Old World – Referring to varieties out of Europe and Asia
- New World – Referring to varieties out of North America
- Heirloom – Typically referring to antique or heritage varieties.
- Scion – the selected apple variety that you plan to graph onto your root stock.
- Hogshead – a unit of measure stemming from the Dutch word Ox-Hooven. Equals about 63 gallons of cider.
- A Barrel – the US standard measurement for beer & cider. Equals 31 gallons
- New England Cider – fermented cider with brown sugar and raisins or grapes. Our New England style is called Hogshead.
- Cyser – A honey cider blend, like our Crabby Granny
- Scrumpy – The English term for craft locally made cider. We have our own Scrumpy!
- Tannic or Tannins – compounds that are produced within the apple that can make for a viscous mouth feel and bittering taste
- Astringent – the dry, puckering mouthfeel caused by a combination of tannins and other naturally occurring chemicals in apples
- Single Varietal – the use of just one variety in the making of a particular cider. We chose the Golden Russet to make our single varietal.
- Racking – to move the cider from one tank to the next so as to clarify and remove the semi-solids
- Piedmont Region – The region in Pennsylvania that our ciders are made, meaning the foothills of the mountains. Typically a great growing region for fruit with fertile well drained soils.




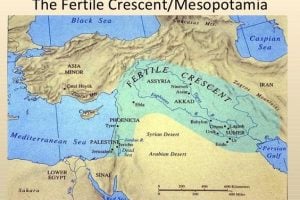
A BRIEF HISTORY OF CIDER
IN ANTIQUITY AND THE OLD WORLD
- 35,000 BC – First known depictions of apples in Paleolithic caves
- Carbonized remains of apples found in Anatolia dating back to 6,500 BC and in Neolithic settlements in what is now Italy and Sweden dating back to 2000 BC
- 8000 years ago apples appear as an article of trade from India to China and the eastern Mediterranean and a cultivated crop in many surrounding lands including Persia, Asia Minor, and Mesopotamia
- Cyser (Honey-Cider) recipes found in Mesopotamian areas
- Roman introduction of cultivated apples leads to explosion in techniques in England
- First recorded references date to Roman times
- 55 BC Romans found the Celtics fermenting their native crab apples
- Techniques spread to the French and Basque regions making Cidre
- 5th century AD collapse of Romans pushed knowledge to protected hands of the Christian monastic orders and the Islamic Moors.
- While French and English get the credit, the Spanish were believed to be making Sidra before the birth of Christ
- Norman conquest re-invigorates the West Country orchards of England and through the 1720’s cider making is led by farmers but the Industrial revolution dampens the quality of cider by pushing it to mass distribution.





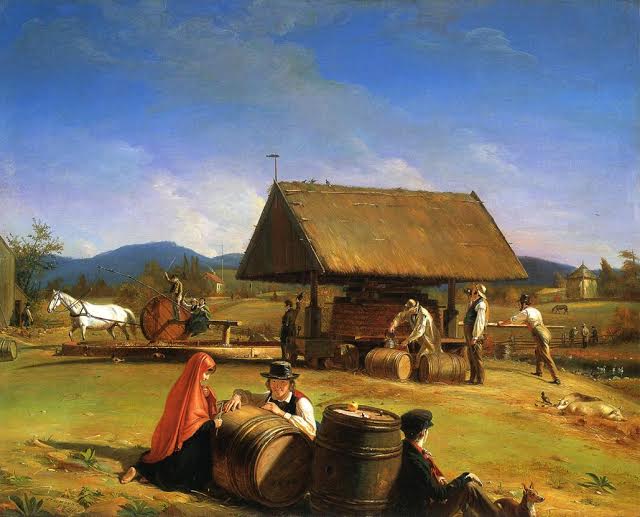
A BRIEF HISTORY OF CIDER IN AMERICA
THE ORIGINAL BEVERAGE OF THE AMERICAS
THE GOOD TIMES
- Apples are the first crops introduced to the new world
- Only native apples are crab
- 1623 First cultivated apples planted in Boston
- Planted by William Blackstone (Blaxton)
- His Rhode Island Orchard introduces Blaxtons Yellow Sweeting around 1640
- The other first cultivated apple of the Americas is believed to be the Roxbury Russet discovered before 1647
- Cider plays the most crucial role in the new economy from the 1640s to 1775 – New England to Georgia
- 1776 New England Historians claim per-capita consumption is 35gallons
- By 1775 – 1 out of 10 farms in New England was a cidery
- President John Adams advertises drinking a tankard of cider every day promotes good health (lives to be 90)
- John Chapman (Johnny Appleseed) born 1774 becomes apple entrepreneur
- Operates nursery in Susquehanna Valley of PA
- Travels throughout PA, OH, and IN preaching and planting
- 1801 New Englanders argue why even bother making beer when cider is so healthy and easy to make
- By the late 1800s, American apples and cider are being exported to Europe
- By 1899 production is at a record 55million gallons of cider a year.

THE BAD TIMES
- 1830’s – Temperance movement brands cider orchards as “demon orchards”
- During the 1800’s many farmers took axes to their orchards and swore off cider
- 1850s – post civil war migration of people looking for work in big cities leaves many cider farms abandoned
- Industrial revolution coupled with urbanization makes beer cheaper to produce
- German immigrants and other northern European immigrants push beer front and center
- More apples being grown for shipping and eating than cider
- Another blow hits 1917-1918 with an unusually frigid winter wiping out orchards
- By the time Prohibition is enacted in 1919 cider production is down to 13million gallons a year
- After just a few years this once proud American tradition is kept alive only by certain farmers and enthusiasts
A BRIEF HISTORY OF APPLE GROWING IN THE BOYERTOWN AREA
THE PIEDMONT REGION OF PENNSYLVANIA
- Golden era about 1845-1872
- Apples were $4/bushel for first grade ($1.50/dozen)
- 1881-1896 down times
- 1881 Transcontinental Railroad put enormous pressure on the PA market.
- Berks County apple grower laments – “scarcely pays to haul out of the orchard to the mills at six cents per bushel
- 1881 Transcontinental Railroad put enormous pressure on the PA market.
- PA Dutch model – single farmstead with the family forming the unit.
- Distinguished by the excellent layout of the orchard compared to the other English, Welsh, Scotch-Irish, etc.
- Keim Orchards and Funks
- 1892 Baumans opens first area press
- 1920s to 1945 – Electricity and engines modernized the farm and orchard.
- Funks, Keims, Shanesville, Ungers, Beekman, Boyertown Fruit Farms (Irey’s)
- 1950’s over 2500 acres of trees in the area
- 1944 – Boyertown Fruit Farms becomes Frecon Orchards
- Purchased from Henry Funk by Richard S. Frecon
- Making apple cider vinegar for the family a favorite past time
- 1951 One of the areas first roadside markets opens by Mary (Sweetman) Frecon
- Besides the apples, pressing and marketing and selling “Sweet Cider” in glass jugs becomes one of the other Frecon products.
- 1960s Frecon brothers Richard and Henry Frecon II start to work on the orchard, with Henry taking the lead on growing operations.
- 1970 First area major farm market retail outlet opens.- by second generation Frecon brothers Henry Frecon II
- 1980’s Henry’s wife Mary Frecon takes on running the retail store.
- mid 2000’s Jenny, Steve, and Hank Frecon all get involved in the operations
- 2009 First area Cidery – Frecon’s Cidery – opens by third generation Frecon brothers, Steve and Hank and their friends Jamie Bock and Josh Smith (husband of Jenny Frecon)
- 2016 Frecon Orchards Ciders makes its debut on the National stage.
EDUCATIONAL LINKS
 |
PA Preferred This resource is a partnership program between the Pennsylvania Department of Agriculture and many companies throughout the commonwealth to support the PA economy and encourage the purchase/support of Pennsylvania made products. |
 |
Penn State – College of Agricultural Sciences, Extension A good resource for tree fruit growers and hard cider producers. The Penn State University (PSU) Extension has been putting together great information and offering events and workshops for industry members. |
| Pennsylvania Apple Marketing Program The marketing board for all things apple-related in Pennsylvania. This resource provides support to apple growers and hard cider makers in terms of marketing. |
|
| Pennsylvania Winery Association Many hard ciders are considered categorized with wine in Pennsylvania. The Pennsylvania Winery Association helps to market wine (and cider) from Pennsylvania, help serve as a resource for wineries with questions about the industry, and make sure the wine industry continually grows locally in PA. |
|
| Brewers of PA Ciders with lower ABVs in Pennsylvania are categorized as beer. Brewers of PA is the association that represents the beer brewers and the beer industry in Pennsylvania fighting for legislative reform and serving as a resource. |
CIDER LIBRARY
Downloadable PDF’s – click to read
Washington State Cider Production Pamphlet
The Emerging Hard Cider Industry – A Market Analysis of the Mid-Atlantic Region
Antique Apples for Modern Orchards
Design and Establishment of a Hard Cider Orchard, Peck
Growing Apples for Craft Cider, Merwin
Sulfur-based Off-flavors in Wine
















